1-介绍
✅ 通过搜索网络回答常见问题 ✅ 在多次调用之间维持对话状态 ✅ 将复杂查询转发给人工审核 ✅ 使用自定义状态控制其行为 ✅ 可以回溯并探索替代对话路径
1)-setup
capture --no-stderr
%pip install -U tavily-python langchain_community演进一个版本: 支持使用外部的搜索工具
"""
基于LangGraph实现的对话系统
本模块实现了一个简单的对话系统,使用LangGraph框架构建对话流程图。
系统支持流式输出对话结果,并可以通过YAML配置文件加载不同的语言模型。
Dependencies:
- langchain_openai - langgraph - typing_extensions"""
import json
from typing import Annotated
from langchain_core.messages import ToolMessage
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
from langchain_community.tools.tavily_search import TavilySearchResults
from base.model_factory import ModelFactory
from IPython.display import Image
class State(TypedDict):
"""
定义对话系统的状态类型
Attributes: messages (list): 存储对话历史的消息列表
使用add_messages注解指定状态更新方式为追加而非覆盖
""" messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]
# 初始化模型工厂和语言模型
mf = ModelFactory[ChatOpenAI]()
mf.load_from_yaml(yaml_path="/Users/carlyu/work/yaww/projects/ai-llm-agent/llm_model_configs.yaml")
llm: ChatOpenAI = mf['doubaoAi']
# 初始化状态图构建器
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)
# 集成搜索引擎工具
tool = TavilySearchResults(max_results=2)
tools = [tool]
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
def chatbot(state: State):
"""
对话节点的处理函数
Args: state (State): 当前对话状态,包含历史消息列表
Returns: dict: 包含新消息的状态更新
""" return {"messages": [llm_with_tools.invoke(state["messages"])]}
class BasicToolNode:
"""A node that runs the tools requested in the last AIMessage"""
def __init__(self, llm_tools: list) -> None:
self.tools_by_name = {it.name: it for it in llm_tools}
def __call__(self, inputs: dict):
# 非空则获取最后一条
if messages := inputs.get("messages", []):
message = messages[-1]
else:
raise ValueError("No message found in input")
outputs = []
for tool_call in message.tool_calls:
tool_result = self.tools_by_name[tool_call["name"]].invoke(
tool_call["args"]
)
outputs.append(
ToolMessage(
content=json.dumps(tool_result),
name=tool_call["name"],
tool_call_id=tool_call["id"],
)
)
return {"messages": outputs}
def route_tools(
state: State,
):
"""
Use in the conditional_edge to route to the ToolNode if the last message has tool calls. Otherwise, route to the end. """ if isinstance(state, list):
ai_message = state[-1]
elif messages := state.get("messages", []):
ai_message = messages[-1]
else:
raise ValueError(f"No messages found in input state to tool_edge: {state}")
if hasattr(ai_message, "tool_calls") and len(ai_message.tool_calls) > 0:
return "tools"
return END
#
tool_node = BasicToolNode(tools)
# 构建对话流程图
graph_builder.add_node("chatbot", chatbot)
graph_builder.add_node("tools", tool_node)
graph_builder.add_conditional_edges(
"chatbot",
route_tools,
# The following dictionary lets you tell the graph to interpret the condition's outputs as a specific node
# It defaults to the identity function, but if you # want to use a node named something else apart from "tools", # You can update the value of the dictionary to something else # e.g., "tools": "my_tools" {"tools": "tools", END: END},
)
# Any time a tool is called, we return to the chatbot to decide the next step
graph_builder.add_edge("tools", "chatbot")
graph_builder.add_edge(START, "chatbot")
graph = graph_builder.compile()
def stream_graph_updates(user_input: str):
"""
处理用户输入并流式输出助手回复
Args: user_input (str): 用户输入的文本
Returns: None: 直接打印助手的回复
""" for event in graph.stream({"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": user_input}]}):
for value in event.values():
print("Assistant:", value["messages"][-1].content)
def _main():
# 主循环:处理用户输入
while True:
try:
user_input = input("User:")
if user_input.lower() in ["quit", "exit", "q"]:
print("Goodbye")
break
stream_graph_updates(user_input)
except:
user_input = "What do you know about LangGraph?"
print("User: " + user_input)
stream_graph_updates(user_input)
break
def debug_graph():
image = Image(graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png())
with open("01.png", "wb") as f:
f.write(image.data)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# debug_graph()
_main()- 增加了一个
tool_node = BasicToolNode(tools), 他的返回是:return {"messages": outputs}这样的结构. - 增加了一条
route_tools条件边决定,集成tools的invoke循环, 最后一条消息如果有tool_calls属性,就去调用对应的工具.
这里的核心上下文内容是通过 内部特殊的 tool_message 封装消息. Debug 内容如下
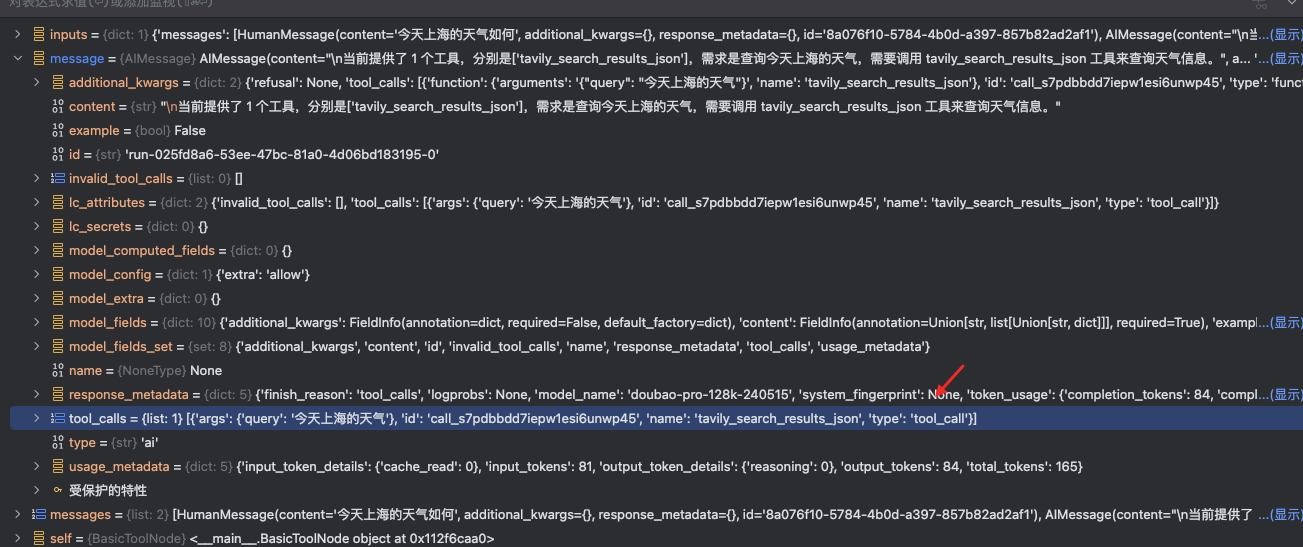
在 langgraph 中已经有预定义的 ToolNode 和对应的 tool_condition .
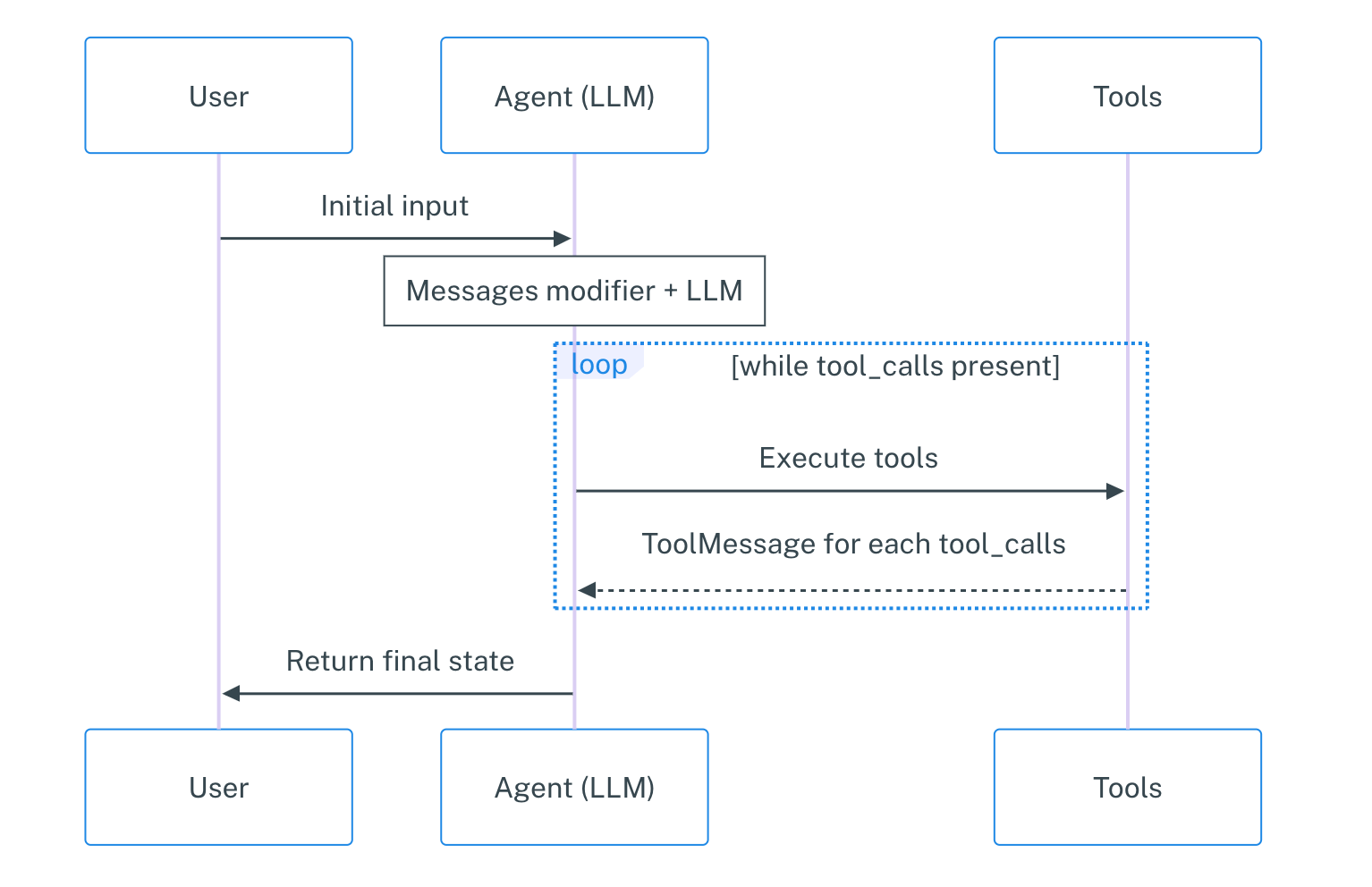
2-3 Adding Memory to the Chatbot
当前的代码中没有 多轮对话的能力.
LangGraph 解决的办法是利用一个 Persistent checkpointing 的机制来优化这个问题. 如果在编译的时候提供一个检查点器 checkpointer 并在调用图的时候提供一个线程 ID (thread_id), langGraph 会在每个步骤之后自动的去保存状态, 让聊天机器人能够自动的从上次停止的地方继续.
Tips
为什么这里要使用检查点机制, 检查点的功能远比 chatbotMemory 强大 - 它允许你随时保存和恢复复杂的状态, 用于错误恢复、人机交互工作流、 time travel interactions, and more.
使用 checkpointSaver 的方法非常的简单.
memory = MemorySaver()
graph = graph_builder.compile(checkpointer=memory)
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "1"}}
def _direct_chat(user_input: str):
events = graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": user_input}]},
config=config,
stream_mode="values",
)
for event in events:
event["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
def _multiple_chat():
_direct_chat("Hi there! My name is Will.")
_direct_chat("Remember my name?")持久化的选择:
- 官方仅仅支持
postgreSql,sqllite的实现 - 官方目前不会考虑支持其他的实现,参考如下的 issue1475